Red-Black 트리
Red-Black 트리는 self-balancing binary search tree이다.
레드-블랙 트리를 포함한 이진 탐색 트리는, 모든 노드에 대해 '자신이 가진 자료는 자신보다 오른쪽에 위치한 부분트리가 가지고 있는 모든 자료보다 작거나 같고, 자신보다 왼쪽에 위치한 부분트리가 가지고 있는 모든 자료보다 크거나 같다' 라는 조건을 만족한다. 이런 특성 때문에 특정 값을 빠르게 찾아 낼 수 있으며, 각 구성원소(elements)간의 효율적인 in-order traversal이 가능하다.
정의

노드는 레드 혹은 블랙 중 하나이다.
Root Property : 루트노드는 블랙이다.
External Property : 모든 리프노드들은 검정(Black)이다.
Internal Property : 빨강(Red)노드의 자식노드는 언제나 검정(Black)이다.
즉, 레드 노드는 연달아 나타날 수 없으며, 블랙 노드만이 레드노드의 부모가 될 수 있다.
Depth Property : 모든 단말노드에서 Black Height는 같다.
어떤 노드로부터 시작되어 리프노드에 도달하는 모든 경로는 리프노드를 제외하면 모두 같은 수의 블랙노드를 가지고 있다.
노드의 Height h일때, black-height >= h/2.
Red-Black 트리는 Binary Search Tree이므로 BST의 특징을 모두 갖는다.
루트 노드부터 가장 먼 경로까지의 거리가, 가장 가까운 경로까지의 거리의 두 배 보다 항상 작다. 이러한 상태를 balanced상태라고 한다. 따라서, 삽입, 삭제, 검색시 최악의 경우 시간복잡도가 트리의 높이(또는 깊이)에 따라 결정되기 때문에 보통의 이진 탐색 트리에 비해 효율적이라고 할 수 있다.
동작
Red-Black Tree에서는 1. Recoloring 2. Rotation 두 가지 방법을 이용해서 균형을 맞춘다. 우선 recoloring을 한 후, recoloring이 불가능해지면, rotation을 한다.
삽입(insertion)
x를 새로 삽입된 노드라고 가정할 것이다.
Binary Search Tree와 같이 노드를 삽입한다. 그리고 새로 삽입되는 노드 x를 RED로 색을 정한다.
만약 x가 root노드이면, x의 색을 BLACK으로 변경한다. (black-height 는 1씩 증가)
x의 부모 색상이 BLACK이 아니거나 x가 root 노드가 아닌 경우

x 의 삼촌노드가 RED인 경우( 속성4 : Grand parent는 반드시 검정색이어야한다. )
부모와 삼촌의 색을 BLACK으로 변경
조상(Grand Parent)색은 RED로 변경
x = x의 Grand Parent로 변경하고 2와 3을 반복해서 진행한다.
x의 삼촌노드가 BLACK인 경우(AVL Tree와 유사)
Left Left Case(case 5)

Left Right Case(case4)

Right Right Case

Right Left Case

예제
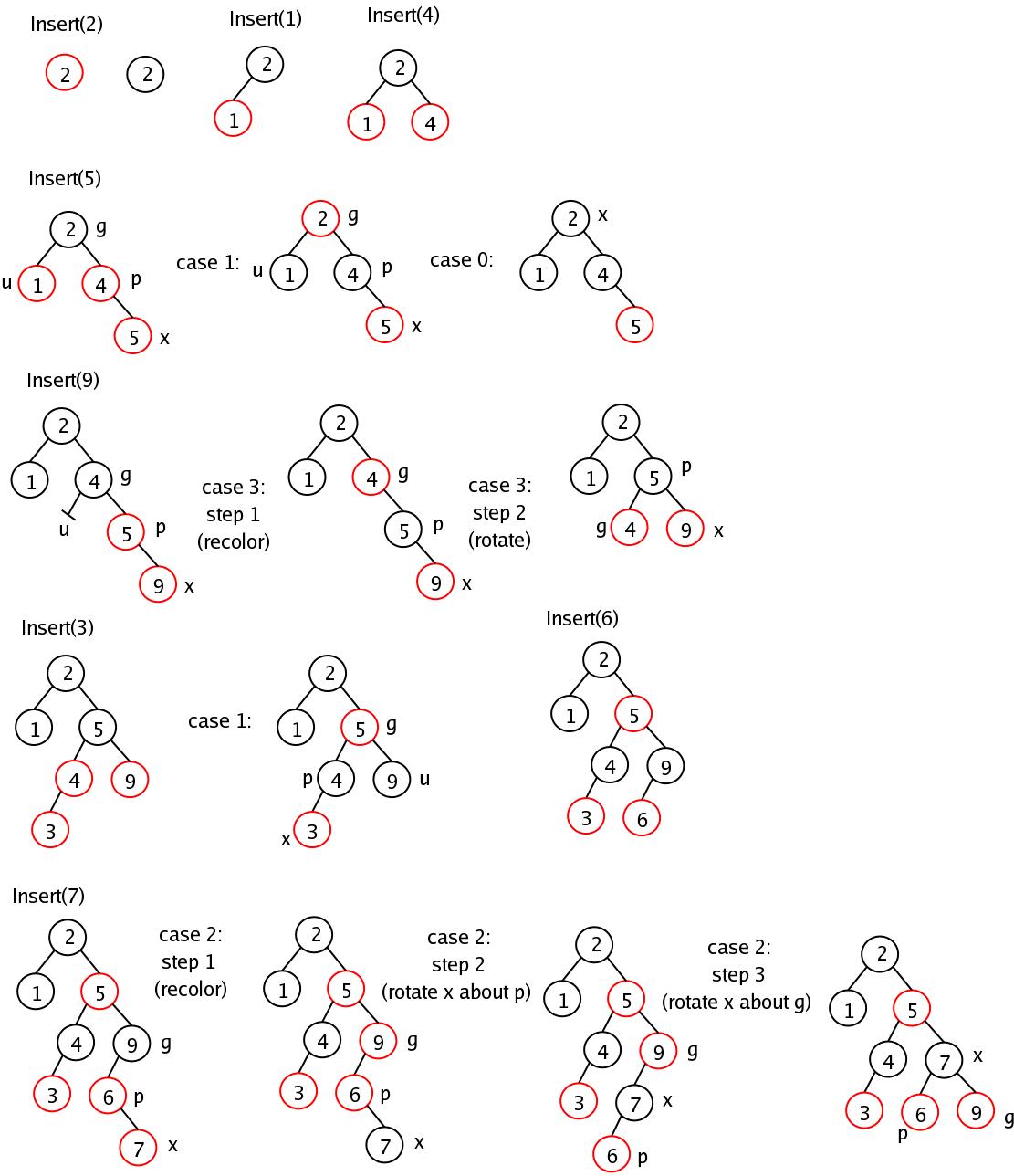
코드
삭제
삽입과 마찬가지로 1. Recoloring 2. Rotation으로 Red-Black의 속성을 유지해야한다. 삽입에서는 삼촌노드의 색을 확인했는데, 삭제에서는 형제노드의 색을 확인해야한다. 삭제는 더 복잡하다. 검은색 노드를 삭제했을 때, 검정색 하위 노드로 대체된다면, 자식노드는 double black이다. 삭제에서 주요한 작업은 double black을 단일 black으로 변환하는 것이다.
삭제할 노드를 v라 가정
BST와 같이 노드를 삭제한다. BST에서 삭제는 자식이 1개이하일때 노드를 삭제하므로 노드가 리프노드이거나 자식이 1개인 경우만 처리하면된다. v를 삭제하고 v를 자식노드로 대체한다
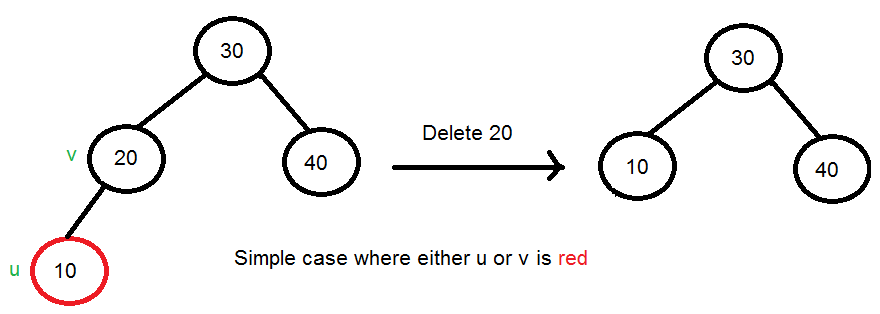
단순한 경우 : 형제노드가 없는 경우(u 또는 v가 RED이면 우리는 대체한 자식노드의 색을 Black으로 바꿔준다.)
형제노드가 있는 경우
Case1 : Node가 새로운 루트가 되는 경우
새로운 루트는 검은색이므로 모든 특성이 보존되므로 통과
Case2 : 형제 노드 색이 Red인 경우, 형제 노드를 Rotate한 후 부모노드와 형제노드 Recoloring한다.
Left Case(Right Case와 반대)
Right Case

Case3 : 형제 노드 색이 Black이고 형제노드의 자식노드가 모두 Black인 경우 : Recoloring 수행
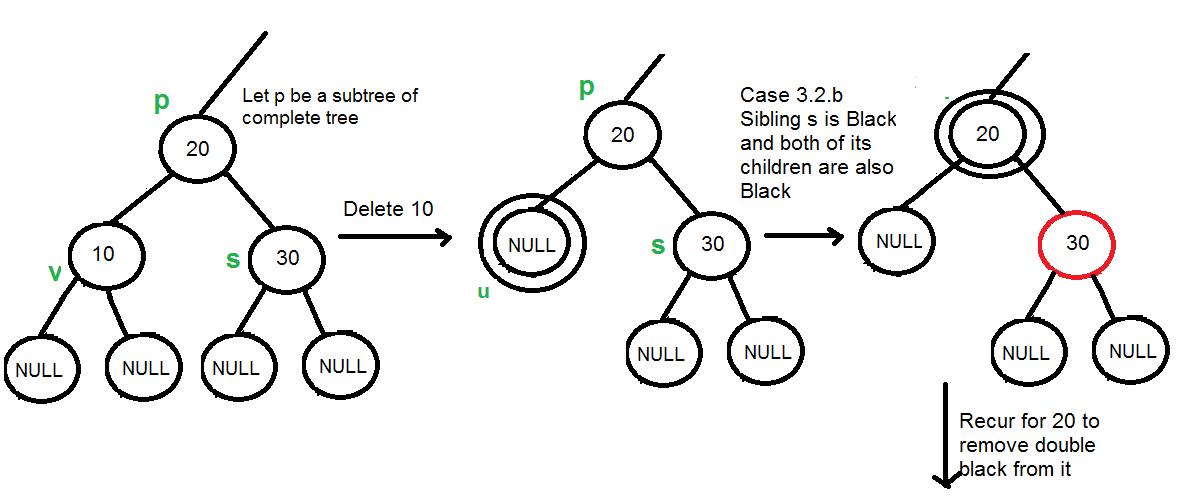
Case4 : 형제노드와 형제노드의 자식노드는 검은색이지만, 부모노드는 빨간색인경우

부모노드와 형제노드의 색을 바꿔준다.
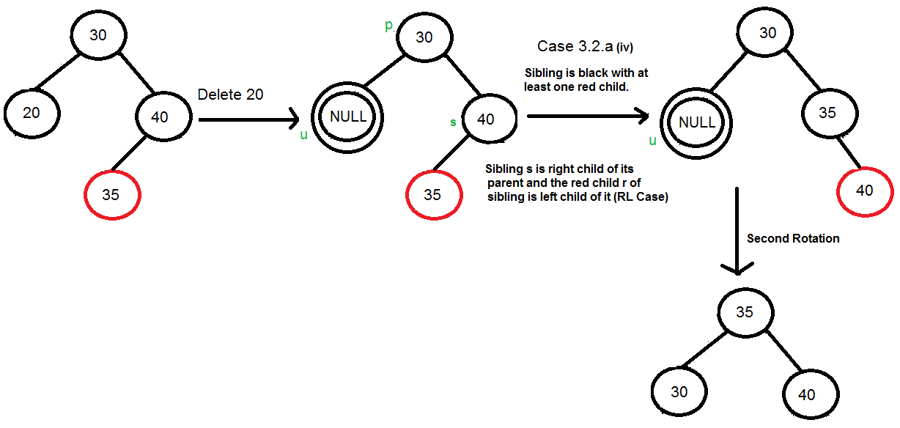
Case5 : 형제노드의 색이 Black이고, 형제 노드의 자식노드 중 적어도 한개의 노드가 Red이면 rotate한다.
Left Left Case
Left Right Case
Right Right Case
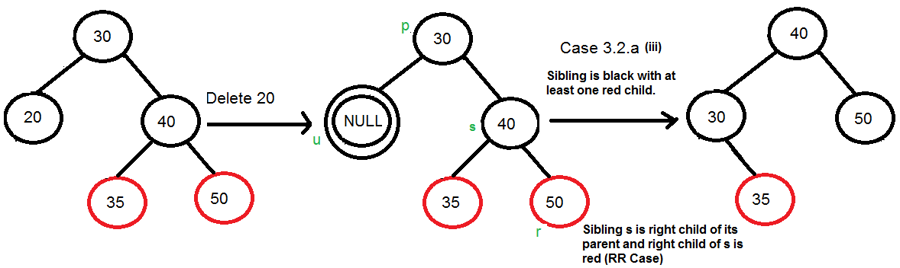
Right Left Case
시간복잡도
Red-Black 트리의 search, insert, delete 연산은 O(logn)의 시간복잡도가 소요된다. 동일한 노드의 개수일 때, depth를 최소화해 시간 복잡도를 줄이는 것이 핵심인 알고리즘이다. 이때 depth가 최소가 되는 경우는 tree가 complete binary tree인 경우이다.
용도
대표적으로 연관 배열(associative array)를 구현하는데 사용한다.
키 하나와 값 하나가 연관되어 있으며 키를 통해 연관되는 값을 얻을 수 있다.
연상 배열, 결합형 배열, 맵(map), 사전(dictionary)으로 부르기도한다.
AVL Tree 와 차이점
AVL 트리는 Red Black Trees에 비해 균형이 잡혀 있지만 삽입 및 삭제 중에 더 많은 회전이 발생할 수 있다. 따라서 응용 프로그램에 삽입 및 삭제가 자주 발생하면 Red Black Tree를 사용하는 것이 좋다. 삽입 및 삭제 횟수가 적고 검색 빈도가 높으면 AVL 트리가 Red Black Tree보다 효율성이 높다.
Last updated